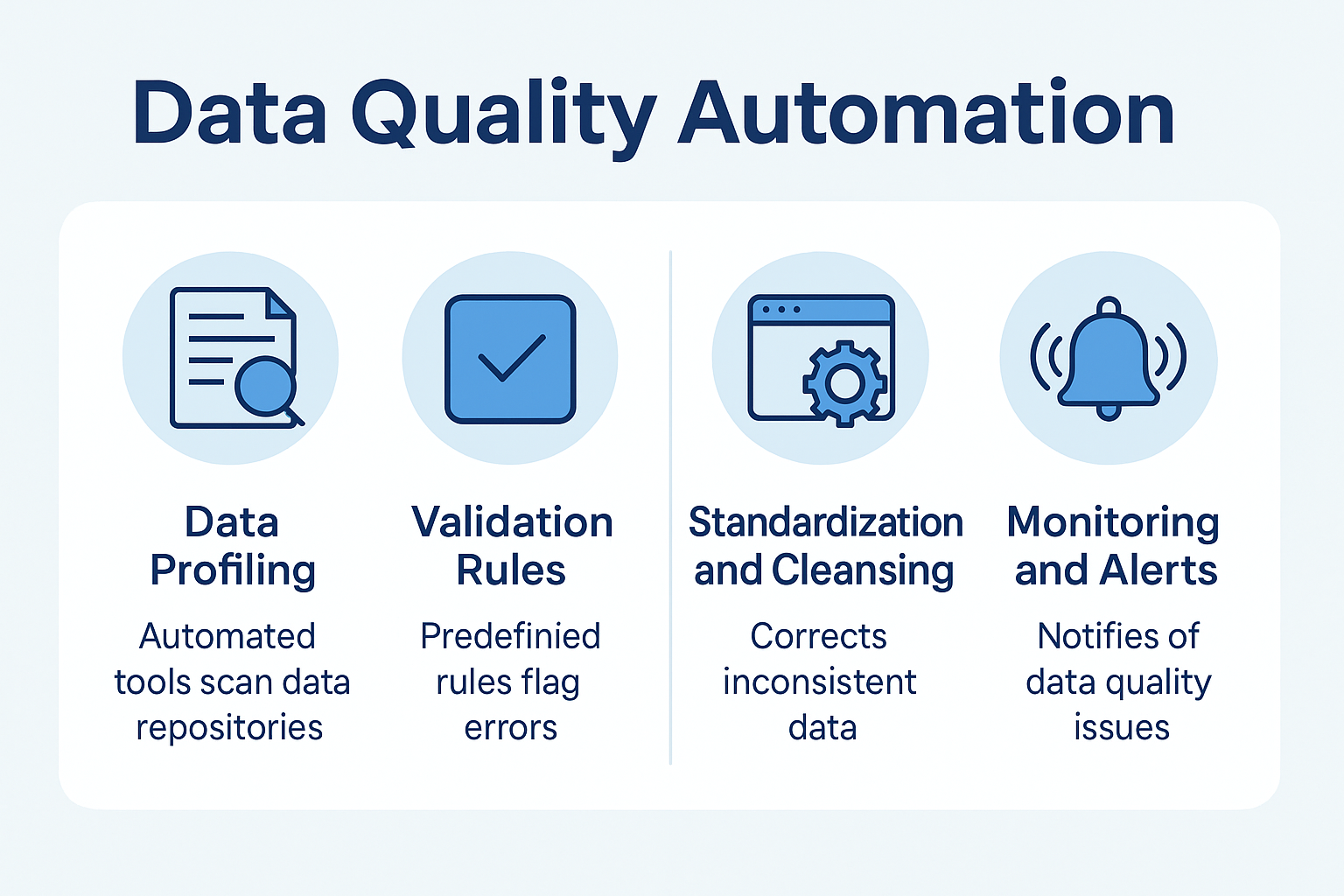
Great organizations continually improve their processes over time, striving to make them as efficient and cost-effective as possible. Business process modeling is a tool that organizations use to evaluate their current processes. It allows the creator to visualize a more efficient process. In this post, we explain how business process modeling techniques give you the knowledge to improve performance across your enterprise.
What is business process modeling?
Business process modeling is a technique that involves creating a visual depiction of a business process. This is typically achieved by using business process modeling tools like flowcharts and universal business modeling process notation (also known as BPMN).
Next, business process modeling is used to identify improvements in an organization’s business processes or workflows. It does this by mapping two different iterations of a given process. The first is the process as it currently exists without implementing any changes. The second is what the process will be once improvements have been made.
It is possible to manually sketch out the steps in a process. This method is, however, far more time-consuming, and less effective than leveraging an automation solution like business process modeling software. With software organizations can easily create and run a process model to identify areas for improvement.
As written in a previous blog post, business process mapping techniques, “you can’t manage what you don’t measure.”
Business process modeling vs business process mapping
The terms business process modeling and business process mapping are often used interchangeably. While the techniques are similar, there is a difference. Business process modeling is generally used to map out low-level processes. In other words, the purpose of the diagram is to provide a somewhat broad overview of how a process works.
Business process mapping, however, can be used to create both broad and highly detailed diagrams. Where maps are detailed, their purpose is to provide operating procedures to guide stakeholders on the efficient completion of a process. Note that both business process modeling and business process mapping are used as part of a broader initiative like business process management.
The benefits of business process modeling
Business process modeling is a highly effective technique that offers organizations a broad range of benefits. Some of these benefits include:
- Identifies areas for improvement. The primary use of business process modeling is to provide stakeholders with a better understanding of the way that a process works with an eye towards implementing improvements.
- Transparency. A business process model shows how tasks are expected to be performed, who is accountable for them, and how a process contributes to the achievement of a business objective. This serves an important role in increasing trust and accountability throughout an organization.
- Agility and flexibility. Business objectives and strategies can change in an instant (think COVID-19). With business process modeling stakeholders can immediately identify and implement improvements consistent with new objectives.
- Standardization across departments. Many processes in an organization, particularly in larger ones, involve similar steps and tasks. For example, purchase order requests are often submitted at the unit level rather than the enterprise level. Using process models, stakeholders can identify best practices across units to implement efficient procedures throughout the organization.
Consider this example of an organization:
“… when reviewing a business process flow chart, a company’s senior management team may recognize that departments that offer incentive programs, such as employee of the week, are more productive than those that do not. As a result, they may choose to provide incentives to employees company-wide.”
Understanding, streamlining and automating processes results in more efficient and more profitable businesses. Through the use of process mapping, information is readily available for important decision making. By graphically depicting workflows, the organization gains transparency in the various workflows throughout the business. Having this information at the ready creates a strong foundation for business agility and speeds the go-to-market efforts for new products and services.
Modeling Elements
Companies use a standardized set of elements provided by the business process modeling notation to model processes. As BPM.com noted in a 2016 white paper, there are four basic types of elements:
- Events, indicated by circles. These can include the start and endpoints of an activity.
- Activities, drawn as rectangles and comprise multiple steps, such as forms and output documents.
- Gateways, identifiable by diamonds. These indicate the various paths an activity can take.
- Sequence flows, marked as arrows (solid, dotted, and so on).
Business Process Modeling Tools
There are many different business process modeling tools that can be used to improve workflows, making them more efficient and cost-effective.
SIPOC Diagrams
A SIPOC diagram is a tool used in the Six Sigma methodology. SIPOC is an acronym that helps stakeholders to identify the key elements of a process improvement project. The elements are the suppliers, inputs, process that is being improved, outputs, and the customers that receive the outputs.
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN)
BPMN diagrams are business process modeling tools that were developed by the Business Process Management Initiative (BPMI). The technique is like UML diagrams and is a standardized method for creating flowcharts – a step by step diagram of a process. Thus, when creating a process model, you use the elements specified under the BPMN methodology.
Unified Modeling Language (UML) Diagrams
UML is a developmental modeling language that is used to provide a standardized way to visually represent a system. Diagrams include a system’s actors, actions, roles, and classes and help to gain a better understanding of or to document a system. UML was created in 1994 and its rapid rise in popularity led to it being published as an approved ISO standard in 2005.
Value Stream Mapping
Value stream mapping is a business process modeling tool used to analyze the existing and future states of a process. These maps show all critical steps as well as the flow of materials and information through a process.
IPO Model
An IPO, or input-process-output model, is a functional graph that identifies inputs, outputs, and required processes. The inputs consist of the information or materials that are introduced into a business process. This triggers the tasks that are required to produce the outputs that are the objective of a business process.
Gantt Charts
Gantt charts are simplistic diagrams that provide a visualization of the overall time taken to complete a task or process. More specifically, Gantt charts can show the start and end times/dates of a process, the required tasks, and how long each took to complete.
Modeling process improvements
As evidenced by the different process modeling tools that we discussed in the last section, there are different ways to utilize the method. There are, however, some general steps that are used when the goal is to improve a process. These include:
- Creating a model of the existing process. This can be done using one of the business process modeling tools discussed above or any of the other dozen or so commonly used techniques.
- Identifying areas for improvement. Process models highlight bottlenecks and inefficiencies in existing workflows. Consider how these issues can be improved and evaluate how the process is operating from an efficiency and cost perspective.
- Creating the new and improved process. Armed with the knowledge that you gained modeling the existing process, implement the changes. Note that with business process modeling software you can test the new process prior to launching it in real-time.
BPM software features
We mentioned above that business process modeling is not a standalone method. Rather it is used as part of a larger initiative like business process management (BPM). As such, a process modeler is an essential feature of a BPM software solution.
A process modeler allows users to design business processes using an intuitive and easy to use drag and drop feature. Users can drag and drop tasks as well as decision points directly on the modeling canvas. Additional elements like forms, users, and data connectors can also be added. It is also important for users to be able to test their new process designs. This is accomplished with a process validation engine. Process validation engines allow users to test their new process designs to ensure they are working prior to deployment.
ProcessMaker offers an industry leading low-code business process management software that gives organizations access to powerful business process modeling tools. ProcessMaker has helped organizations around the globe to transform their business processes.