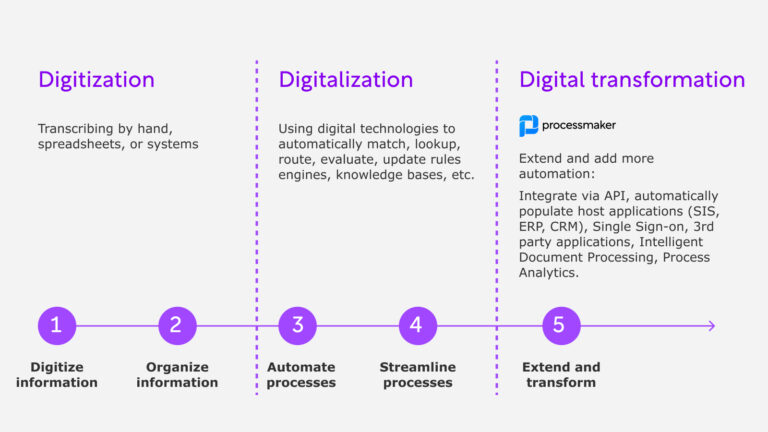
Most companies are familiar with the theories of business process management (BPM). New tools are making it possible to automate process flow to maximize efficiency and increase outputs. However, business decision management (BDM) is not implemented as broadly. These two concepts are entirely separate yet complementary. Innovative organizations use both to revolutionize how business is done.
The Basics of Business Process Management
Every business has processes in place, from production line procedures to human resource transactions. However, some of these processes are more formal than others. For example, technical manuals might detail how and when to use customer relationship software. However, the basic production steps are shared by word of mouth.
Business process management or BPM is the science of breaking each process down to its most basic steps and documenting the processes from start to finish. Through documentation and data examination, it is possible to locate areas that require modifications for greater efficiency.
Organizations that adopt BPM software find opportunities for continual improvement. In many cases, you can automate transactional processes. This makes it possible for staff members to focus their efforts on activities that add significant value to business operations.
The extent to which processes can be automated depends on the types of decisions that come up as the process is completed. Complex decisions often require input from staff members — particularly when there is no formal decision-making process framework in place. The more input necessary from employees, the less likely that the process can be automated in a significant way.
The Basics of Business Decision Management
Many leaders consider operational decision-making as much an art as it is a science. They evaluate relevant data and determine whether to move forward on projects. Such projects include new marketing campaigns, new product lines, and new human resource initiatives based on their knowledge and experience. Often, this method of decision-making runs throughout the business.
Subjective criteria and personal opinions determine the path forward. Whether a change in suppliers is needed or there is an opportunity to update business processes, there are no established decision rules to guide decision-making. As a result, outcomes are inconsistent and unpredictable.
Business decision management brings objectivity to decision-making by defining criteria objectively, standardizing each step, and automating the process. BDM encompasses all operational decision-making systems in a business. However, it primarily manages interactions with customers, suppliers, and employees.
BDM requires compilation and careful analysis of historical data to guide future decisions. Additionally, it takes the guesswork and debate out of decision-making. This results in a streamlined, effective, automated selection process. The foundation of BDM is a business rules management system (BRMS): software capable of gathering and referencing the data needed to make appropriate consistent decisions.
The Setup
During setup, the software is given defined parameters for decision logic. It then deploys to assigned processes. The software monitors and manages the many inputs to decision-making from across the organization, and it executes on decisions as necessary. The user defines business rules to build a logical system. These may include documented policies, requirements, and procedures, as well as clear conditional statements. For instance, take this example of a conditional statement: “If the customer has not placed an order in six months, then an email is sent offering a discount on the next purchase.” Of course, such statements are written using language that the software understands. Often, the system will use FEEL (friendly enough expression language).
Amazon is a leader in automated decision-making for customer contact. The system decides when marketing emails are appropriate for a particular individual. The system pitches an item that will likely appeal to the customer based on past purchases. This pitch is based on wish lists and products that the customer has recently viewed. When the decision model shows that customers qualify for more than one marketing message, the decision management software selects the most appropriate message at that moment. Doing this avoids instances of inundated email boxes.
The Role of Decision Modeling in Business Decision Management
Before a BDM system becomes truly effective, business leaders must carefully break down and define each input for a given decision. The resulting decision modeling diagrams take all possibilities into consideration, so the software can make the most appropriate decision in a given situation. This is a lengthy process, particularly when a larger decision is dependent upon dozens of smaller decisions.
Object Management Group works to standardize the decision modeling process with a comprehensive system for notation and representation of decision models across organizations and industries. The standardized decision model and notation (DMN) permits easy sharing of best practices and greater collaboration among users.
The combination of high-quality automated business decision management and business process management is a concept often referred to as “intelligent process automation.” By gathering historical data and analyzing it, smart technology can learn to choose the appropriate next step based on what works. This promises to transform the efficiency and effectiveness of your business.
ProcessMaker is a BPM business process management software that allows you to incorporate business decision management to ensure automated, data-driven decision-making. ProcessMaker offers a free trial period so you can explore the possibilities for your company today.