Organizations may pick from a variety of innovative process transformation and automation solutions. AI, BPA, and ML are three of the most often used acronyms in the modern information technology business. RPA and BPA are both acronyms for process automation technologies, which may boost workplace productivity and efficiency.
For instance when robotics process automation is not utilized in isolation, it is typically incorporated into business process automation. Investigate these two concepts in further detail to see whether they have the potential to boost your company’s profitability. Although these two terms have distinct meanings, they are frequently used interchangeably.
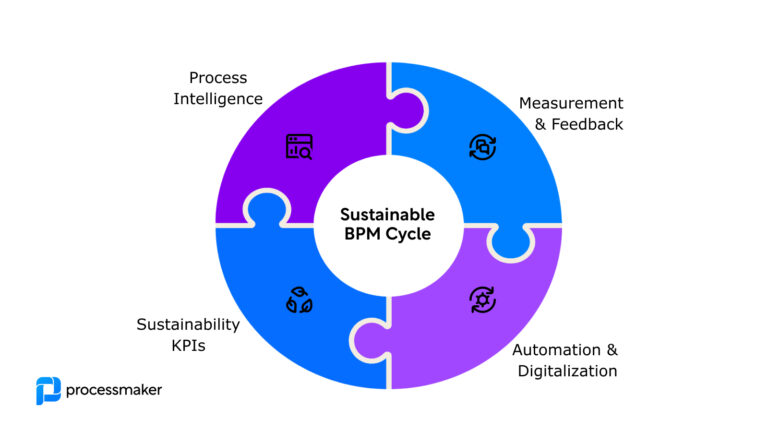
How Business Process Automation (BPA) differs from RPA
When company activities are automated, workflows become more efficient (BPA). Rather than concentrating on a particular department, BPA is developing software solutions that integrate all of its current programs. BPA employs a comprehensive approach to avoid entanglement in a single part of the process.
However, a thorough examination of the organization’s inefficiencies is typically necessary to uncover the most critical concerns when it comes to business process automation. As a result, these activities are built on the pillars of company operations, ranging from speedy account opening to the real-time delivery of promotional offers to prospective clients.
Business procedures enable several departments to interact more effectively and profitably. BPA, for example, is utilized as the backbone for both an enterprise resource planning (ERP) and a customer relationship management (CRM) system. These benefits of business automation may be achieved while spending less money, increasing employee productivity, and creating happy customers.
BPA key takeaways:
- Businesses that adopt a more comprehensive approach to efficiency improvement may benefit.
- It augments the overall efficiency of an organization comprehensively.
- Businesses must conduct an in-depth audit of their operations to ensure compliance with the BPA’s guidelines.
- The BPA system is unique because it was created from the ground up.
How does RPA operate precisely?
According to a Deloitte survey, around 95% of business respondents want to use RPA to increase productivity. RPA software enables the creation, deployment, and operation of self-driving software robots that mimic human behavior and interact with digital systems and software. As with people, software robots may do various activities simply by interpreting what they see on the screen and selecting the appropriate buttons. Because software robots do not need to get up and stretch or grab a cup of coffee, they are still quicker and more trustworthy than humans.
Additionally, automation of robotic processes increases efficiency, responsiveness, and productivity. Also, eliminating tedious tasks from the workday provides various benefits, including increased productivity and a more balanced work-life balance for employees.
Further, RPA is non-intrusive and, when applied fast, can accelerate the pace of digital transformation. Another advantage of this technology is automating activities on systems that do not have APIs, virtual desktop interfaces, or database access.
Using RPA vs BPA to automate
Data entry and file transmission are two jobs that software robots could perform in place of humans. These individuals can fill out forms, perform regular analyses, and generate reports. Robots may be taught cognitive skills such as interpreting language, talking and analyzing unstructured data using advanced machine learning models.
By automating repetitive, high-volume tasks, humans may focus on their core competencies, such as innovation, collaboration, manufacturing, and customer service. Increased productivity, efficiency, and adaptability help businesses. RPA is a foregone conclusion in terms of the future of work.
- Both BPA and RPA seek to automate business processes. BPA was the first to provide RPA capabilities to its clients during its early stages. Integration, procedures, and cost are the primary contrasts between BPA and RPA.
- RPA, as a tactical approach to large-scale automation, has the potential to automate routine and manual activities in massive enterprises. They complement one another well and may be part of a broader modernization drive motivated by need and economic gain.
- RPA and BPA can improve the effectiveness and productivity of a business’s process. In comparison, both organizations rely on a variety of automated processes.
RPA bots running on desktop computers may take advantage of the present user interface to do human-like actions such as copying and pasting, transferring files, and sending emails. Without human assistance, the bot records and replicates the whole operation. Although there are few examples of intelligent bots, the vast majority of bots have not yet reached this level of intelligence. Bots commonly grab data from internet forms using a process called screen scraping.
On the other hand, BPA makes it more challenging to develop workflows that integrate a broad range of systems using a standard processing paradigm. These systems require APIs and database access to exchange and extract data. Coding and development support is needed to perform this job quickly and efficiently. RPA enables computers to record, learn, and perform tasks independently. RPA is not dependent on the use of an API.
As a result, integration using BPA takes a more thorough approach to the problem. Simplifying a business’s decision-making process is beneficial. RPA’s primary objective is to automate time-consuming human tasks. Because RPA is compatible with pre-existing BPA software such as ERP and CRM, it does not influence day-to-day company operations.
One use of RPA in CRM is chatting windows on websites. I can automate your chat windows for you if you so choose. These bots send the information they collect to a human employee, who interacts directly with the consumer. Bots are widely used in procurement automation to do tasks formerly performed by humans, such as form filling, email analysis, and building vendor-specific forms.
In addition, BPA is slightly intrusive in terms of integration. It is possible to construct a new system by replacing it with self-contained and running its software. Each division of BPA is connected by a single system, which simplifies and automates the whole process. The BPA is responsible for ensuring that all operations run smoothly.
Advantages of combining the two process automation technologies
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a subset of BPA that enables optimizing critical business processes (BPA). When combined with RPA, this approach generates considerable commercial benefits while maintaining the efficacy and safety of RPA. Rather than RPA, BPA emphasizes the strategic and tactical advantages of automation.
Authorization of invoices is performed utilizing software solutions such as RPA, and vendor compliance and performance are evaluated.
Hence, BPA’s primary role is to establish the company’s objectives and provide guidance on accomplishing them. Business Process Automation (BPA) can be used to automate P2P if it is used to analyze and improve existing P2P activities. Automation of processes and system choices are included. Following the approach’s adoption, the outcomes will be examined with any further adjustments. Among the several benefits of RPA over conventional techniques are the automation of low-value and repetitive tasks and faster and more accurate invoice processing.
Due to the commercial benefits of RPA and BPA, enterprises worldwide are implementing digital transformation initiatives to automate processes and gain a competitive edge. By migrating from a manual to a cloud-based platform, You can significantly increase efficiency and production.