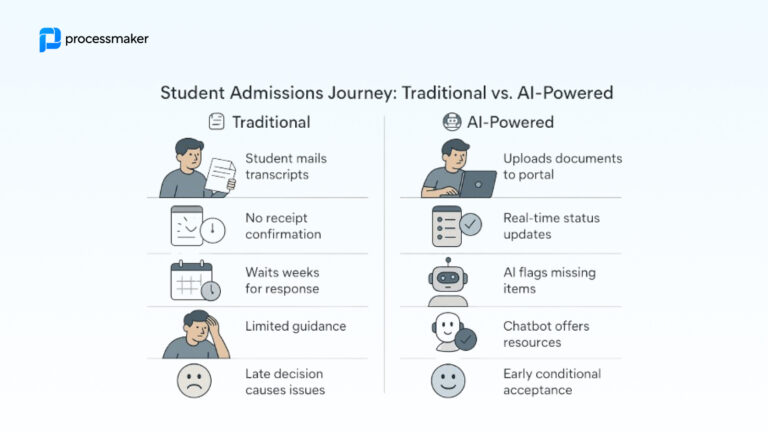
AI has been at the forefront of technological discussions for years now. We’ve heard about AI’s impact on job displacement, the ethical considerations of machine learning, and the future of AI-driven innovation. However, one critical aspect that often goes unnoticed in these discussions is AI inclusivity, particularly for non-technical teams. While the tech-savvy professionals and AI enthusiasts are grappling with the implications of artificial intelligence, there is a growing group of workers who are being left behind in the rush towards automation: the non-technical workforce.
The Reality of AI Anxiety in Non-Technical Teams
When we think about AI, our minds often gravitate toward the world of engineers, data scientists, and tech professionals who are building the future. But for many non-technical employees, AI can be a source of anxiety. These employees may be unfamiliar with AI concepts and the technological landscape. The constant headlines about AI replacing human jobs can be overwhelming, and it raises legitimate concerns.
Imagine working in a role for decades, feeling secure in your expertise, only to be suddenly told that AI is taking over your responsibilities. For non-technical workers, this shift can be especially alarming. Older employees, individuals with limited technical training, or those who struggle to grasp complex concepts may feel excluded and vulnerable in a world where AI is poised to revolutionize everything.
The Vulnerability of Non-Technical Groups
While headlines celebrate AI breakthroughs and productivity gains, they often overlook the human cost of rapid technological change. The most vulnerable groups facing AI displacement include:
- Older workers (50+ years): Many have built careers on expertise that took decades to develop. The prospect of learning entirely new AI-powered workflows can feel overwhelming, especially when coupled with age discrimination concerns in the job market.
- Workers in traditionally stable industries: Manufacturing, retail, customer service, and administrative roles that remained largely unchanged for decades now face AI disruption. Employees who found security in routine work suddenly confront an uncertain future.
- Natural technical disinclination: Some individuals may simply not be inclined to engage with technology and may find it difficult to understand the nuances of AI.
- Geographical and industry differences: In certain regions, industries, or roles that have remained unchanged for decades, AI adoption may seem like an insurmountable challenge.
This gap in understanding and capability is creating a divide in the workplace, and non-technical workers often feel like they’re on the losing side of the AI revolution.
The Seriousness of the Problem: Mental Health and Well-Being
The impact of AI anxiety on well-being cannot be underestimated. As AI and automation start to encroach on jobs, the following mental health issues are becoming more prevalent:
- Stress and depression: The fear of obsolescence or having to adapt to new technologies can cause significant stress.
- Fatigue and burnout: The pressure to learn new skills quickly or adapt to unfamiliar tools can lead to exhaustion.
- Imposter syndrome: Non-technical workers may feel that they are inadequate or incapable of learning AI-related concepts, leading to feelings of imposter syndrome.
- Workplace-related suicides: In extreme cases, the anxiety and stress caused by rapid technological change can have devastating consequences.
While the link between AI disruption and suicide may not be immediately obvious, the profound impact on self-worth and identity is real. For those who have built their lives around a job they’ve done for decades, a sudden change or loss of job security can lead to a crisis that is hard to recover from.
Tangible Obstacles Non-Technical Teams Face with AI
Understanding AI is not just about technical knowledge—there are several tangible obstacles that non-technical teams face when encountering AI:
- Trust issues: AI is seen as an unfamiliar, mysterious entity. Trust in AI may be lacking, especially when employees don’t understand how it works or what it is doing with their data.
- Complex terminology: Many AI tools are built with technical jargon, making them inaccessible to those without a background in the field. Non-technical workers often struggle to grasp these complex terms, making AI seem like a distant and irrelevant concept.
- Lack of simple tools: While there are AI tools designed to improve productivity and streamline workflows, many of them are too complicated for non-technical users. They may seem perfectly simple and easy-to-use for those who develop or procure them, but the story could be different for those who actually use them (especially the vulnerable groups listed above.)
Strategies to Make AI Inclusive for Non-Technical Teams
To address the challenges non-technical workers face, it’s important to implement strategies that bridge the knowledge gap and make AI more inclusive. Here are some key approaches:
- Simplify AI tools and terminology: AI tools need to be designed with non-technical users in mind. This means creating intuitive interfaces and using plain language, rather than complex jargon, to explain how the tools work. Even if something feels as intuitive and simple as possible for designers and developers, that may not be the case for non-technical users.
- Provide accessible training: Training programs should be tailored to non-technical teams, focusing on fundamental concepts and practical applications rather than deep dives into algorithms or coding.
- Incorporate AI into existing workflows: Rather than asking workers to completely change their ways of working, AI should be integrated into existing workflows in a way that enhances rather than disrupts the current processes.
- Build trust through transparency: AI systems should be transparent, with clear explanations of how decisions are made. Non-technical workers need to feel confident that the technology is not working against them but rather supporting their roles.
- Encourage collaboration between technical and non-technical teams: Cross-functional collaboration can help break down the barriers between technical and non-technical employees. By involving non-technical teams in the design and implementation of AI tools, organizations can foster a sense of ownership and empowerment.
The Need for AI Democratization
In our pursuit of technological advancements, it’s easy to forget that not everyone is equipped to adapt to the changing landscape. Many professions, industries, and regions have not historically been involved in the tech revolution, and introducing AI to these areas requires a thoughtful, inclusive approach. The key to a successful AI future lies in democratizing AI, making it accessible and understandable to everyone, regardless of their technical expertise.
By recognizing the challenges faced by non-technical teams and addressing these issues with empathy and strategic planning, we can create a future where AI works for everyone—not just the tech-savvy few. It’s essential to bridge the gap, provide the right tools, and ensure that no one is left behind in the age of artificial intelligence.
Read more about Agentic AI:
Whitepaper: Agentic AI at ProcessMaker
Agentic AI in Process Automation
Organizational Readiness for Agentic AI
Ethical Considerations of Agentic AI
Barriers to AI Adoption in Business Process Automation
The Perfect Partnership of BPA and AI
Unlocking the Full Potential of AI: Why Task Mining is Your Secret Weapon
Use cases:
5 Ways Agentic AI Transforms Employee Experiences
Automation in Investment Analysis: How Agentic AI is Transforming the Industry