Many large enterprise businesses are in the process of implementing global business services (GBS) or have plans to explore them in the near future. Establishing a strategic framework for GBS is crucial for linking process improvements and service innovations to measurable business outcomes that contribute to overall business objectives and value creation. In this article we go through what they are, what are their benefits and what enterprise leaders need to know to get started with GBS in 2023.
What are global business services?
Global business services (GBS) is a term used to describe integrated, shared services that are used to support business units and organizations around the world. These business solutions centralize key functional services and enhance effectiveness through a multifaceted approach.
GBS can include a variety of services, such as finance, accounting, human resources, marketing, information technology, and customer service. GBS may be used to streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve efficiency in global organizations.
Infographic: which services does GBS currently provide and which services are you planning for the future?
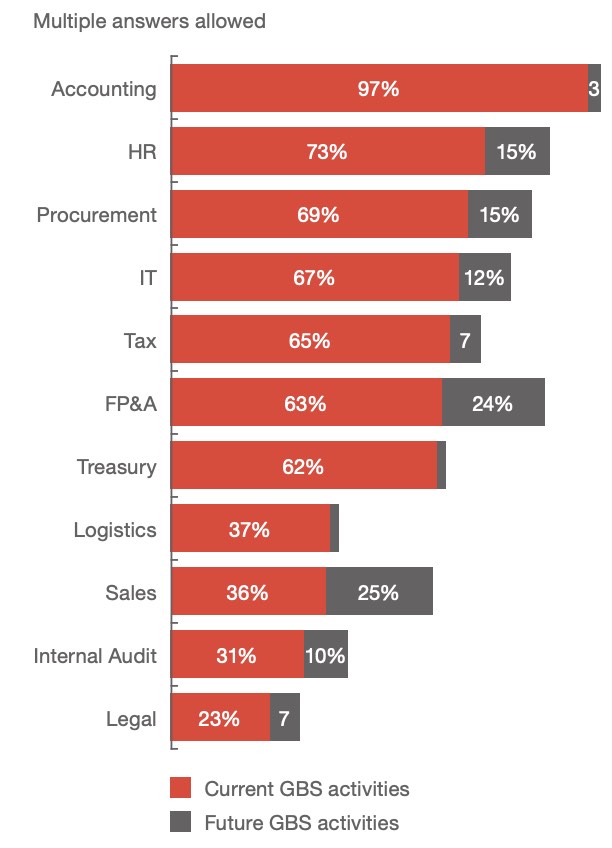
Source: PwC Global Business Services – Key to Agility Study 2020
GBS vs Shared Services and Business Units
The main difference between GBS and shared services is that GBS is focused on providing integrated services to business units and organizations around the world, while the shared services model is typically focused on providing services to a single organization. However, evolving from a basic shared services model to a more integrated Global Business Services (GBS) framework can unify these functions to enhance optimization and strategic value.
Another perspective is in terms of organizational maturity. GBS can be seen as an advanced implementation of shared services. GBS may be more complex than shared services, as it must account for different legal, cultural, and language issues around the world. GBS can also be more expensive than shared services, as it requires more resources and infrastructure.
GBS and Centers of Excellence
While they are not often confused, global business services and global centers of excellence (CoEs) may be complimentary in advancing operational excellence. Key components of this operational excellence include critical elements such as a customer-centric interface, an agile center of competence, and a global network of shared delivery platforms.
The main difference between GBS and Centers of Excellence (CoE) is that GBS focuses on providing integrated services to business units around the world, while CoEs are focused on providing specialized and centralized expertise around a technology (eg. around process intelligence, intelligent automation or RPA.)
GBS can help organizations achieve greater scalability and flexibility, while COEs can help organizations become more competitive by leveraging their specialized expertise.
Top risks for GBS organizations
According to Hackett Group research from 2024, the top strategic risks for GBS organizations are shifting from the cost of labour being at the top to talent shortage taking the lead. Employee turnover risk is another critical risk that has an especially high impact for shared services organizations.
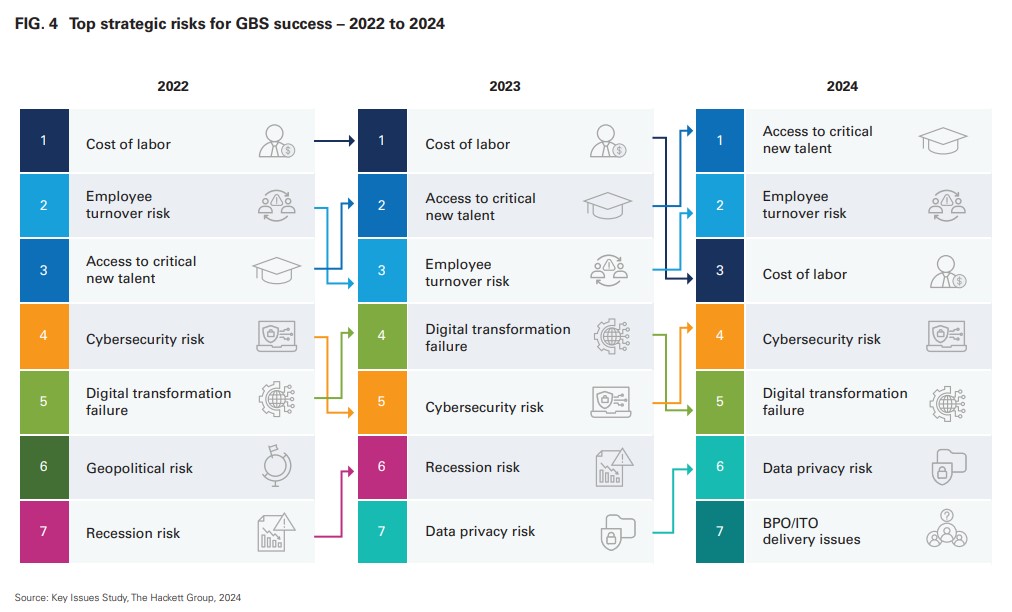
Source: The Hackett Group Report on GBS Agenda 2024
5 key advantages of GBS
Business organizations can gain a number of advantages from adopting a GBS strategy.
- Advance digital transformation. GBS can align and increase the adoption of modern digital tools and digital capabilities, enhancing business processes.
- Increase customer-centricity. Organizations that leverage GBS can improve the customer experience by aligning different business processes to the benefits of the customer.
- Improve work (and work satisfaction). Organizations that leverage GBS can ensure that their workforce are equipped with the right tools and skills for modern digital work.
- Data-driven decisions. Organizations that leverage GBS are able to utilize data and analytics more in decision making.
- Positive performance benchmarking. As organizations adapt GBS they can leverage internal competition and benchmarking to make sure different teams are aligned with best practices.
Typical goals and targets of GBS
Certain fundamental goals have been at the very core of the GBS organizations and remain to be in priority even amid these changing times. Some common goals for GBS implementations include the following.
- Reduced costs. This is one of the most critical factors for shared service centers. GBS organizations are taking over a wider variety of activities, while companies are still expecting good results. Keeping costs low while increasing operational effectiveness is a challenge in itself. Successful GBS organizations deliver strategic value, positioning themselves ahead of their peers and providing a competitive advantage.
- End-to-end visibility and alignment. Many GBS functions benefit from the standardization and alignment of key business processes.
- Improved and streamlined processes. Improving the processes and implementing the best practices throughout an entire organization over different geographic locations is another critical goal for GBS.
- Agility and continuous improvement. GBS functions can be quicker to respond to global disruptions and be more effective in achieving continuous operational excellence.
- Supporting enterprise’s growth initiatives. Although GBS organizations don’t necessarily bring profit in its conventional meaning, perceiving them as more than just a cost reduction center is a good practice. Through continuous improvements in end-to-end processes, investments made into shared centers might significantly impact other business areas as well, beyond that of GBS.
GBS and Intelligent Automation (IA)
GBS can use intelligent automation to achieve process efficiencies, streamline operations, and reduce costs. Intelligent automation can be used to automate repetitive tasks, such as data entry, to improve productivity and efficiency. Additionally, GBS can be used to leverage the power of artificial intelligence to gain insights into customer behavior and optimize operations, or robotic process automation (RPA) to fully automate repetitive tasks.
Infographic: what are current levels of automation within your GBS?
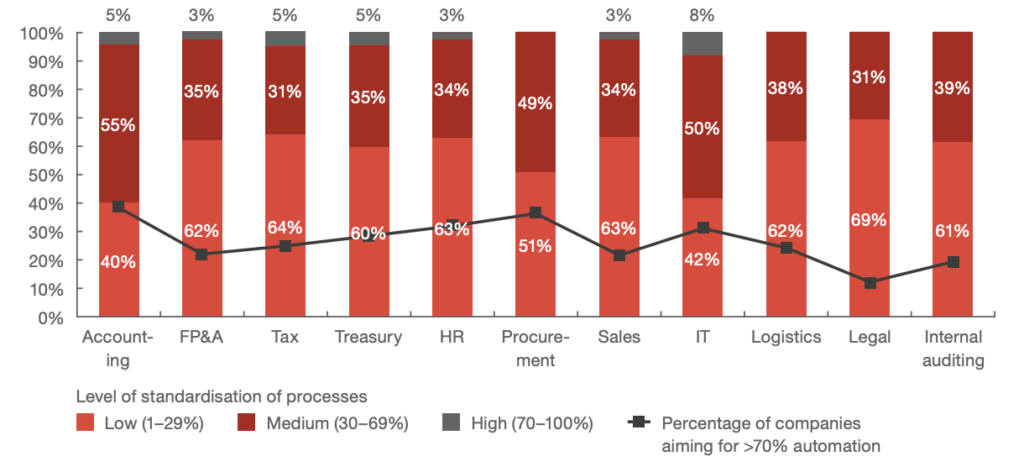
Source: PwC Global Business Services – Key to Agility study 2020
Several intelligent automation technologies have been adopted by GBS organizations in the past few years. Among them are RPA, Intelligent Data Capture, Chatbots, and Generative AI. Despite the fact that expectations on business outcomes were not fully met, there’s an adequate growth projection for many of these technologies.
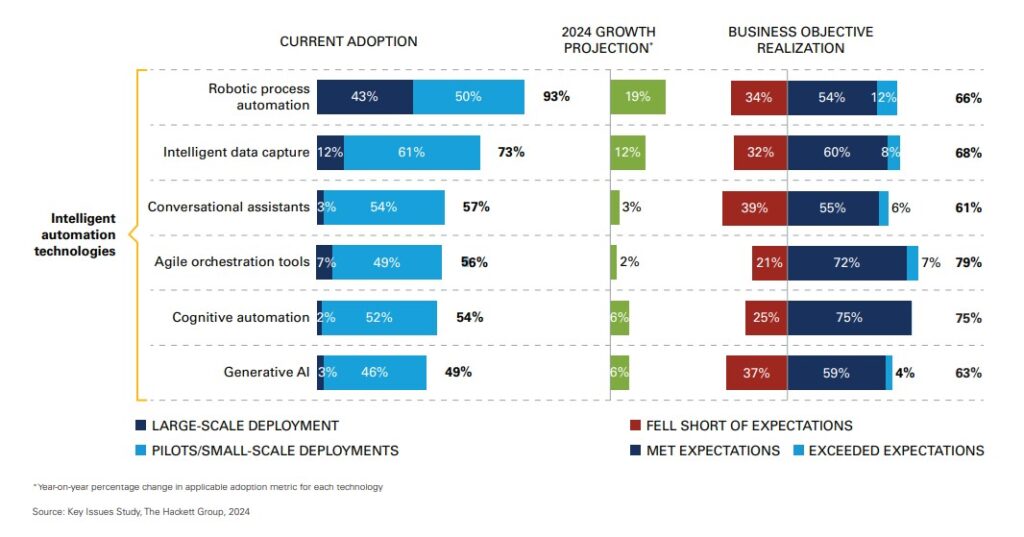
Source: The Hackett Group Report on GBS Agenda 2024
GBS transformation challenges in 2024
There are a plethora of different challenges GBS organizations face regularly but these are the most common and impactful ones.
- Organizational resistance to change. According to the Hackett Group report on GBS Agenda in 2024, change resistance remains to be a top hurdle that hampers GBS transformation in the recent years.
- Resource dependency. GBS centers don’t generate profits and have to rely on the parent organization. A large portion of the costs for GBS organizations comes from salary expenses, as most of the SSC functions are highly labor-intensive. GBS transformation involves evolving support functions and achieving effective platform deliveries, which only about 5% of companies manage to reach.
- Ununified governance. The overall effectiveness of GBS centers might suffer if there’s no consolidated governance that helps share the best practices in utilizing technologies and tools across different units and locations.
- Not readiness for automation. GBS center’s infrastructure should facilitate the automation of processes in the first place. The unit shouldn’t be too siloed, it should have a goal- and growth-oriented team culture and transparency among team members.
- Lower efficiency with increasing headcount. More people is not a solution; that’s the bitter truth for all types of companies, not only GBS. The best way out would be to leverage the advanced technologies for the right processes and at the right time.
- Coming up with mid-term goals. Going visionary is important but knowing which tools and technologies are relevant to the overall business in the near future shouldn’t be neglected. Many times companies waste time and money pursuing the wrong larger goals without
Adapting to Covid and new ways of work
Covid has changed a lot in the way companies operate, and significant changes have touched GBS organizations as well. GBS teams are fostering global collaboration and driving significant business outcomes through agility and a customer-centric approach. From being more location-specific and driven by cost-effectiveness, they’ve been paving their way towards becoming front runners in adopting new technologies and tools to support and augment workers and implement best practices.
GBS organizations are expanding their portfolio of offerings to serve core businesses worldwide. That being said, certain challenges always come in the way, so there’s a clear need for continuous improvements in quality that drives cost-efficiency. This article will expand on the main GBS targets in 2022 and the challenges they go through on the journey to become more effective.